Your grinder pump suddenly stops working, and wastewater starts backing up into your lowest drains. This emergency situation requires immediate action to prevent sewage from flooding your home. Grinder pumps are critical waste management systems for properties that can’t rely on gravity to move wastewater to septic tanks or sewer lines. When these specialized pumps fail, they create unsanitary conditions that demand prompt attention. This guide provides specific troubleshooting steps to diagnose and resolve common grinder pump problems before they escalate into costly disasters.
Understanding how your grinder pump processes waste helps you identify problems faster. These systems use motorized cutting blades to transform solid waste into a smooth slurry that travels through small-diameter pipes, even uphill. When issues develop, recognizing the warning signs early—like unusual noises, frequent breaker tripping, or alarm activation—can save you thousands in repair costs and prevent the gross inconvenience of sewage backups in your home.
Diagnose Immediate Grinder Pump Failure Symptoms
When your grinder pump stops working completely, wastewater backs up into showers, sinks, and toilets within hours. This emergency situation requires systematic diagnosis to determine whether you can implement a quick fix or need professional help immediately.
Identify Performance Degradation Warning Signs
Noticeable performance drops often precede complete pump failure. Constant running occurs when your pump operates longer than normal or fails to shut off after completing its cycle. This symptom typically indicates dull blades struggling to process waste or a malfunctioning float switch stuck in the raised position. When your pump runs continuously, it works harder than designed, accelerating wear on internal components.
Reduced grinding efficiency shows when your system struggles with normal wastewater volumes that it previously handled effortlessly. Diminished performance often stems from worn blades, internal component deterioration, or developing clogs restricting normal operation. Cold weather can also cause performance issues when wastewater freezes within the system, creating immediate flow restrictions.
Recognize Sensory Warning Indicators
Your grinder pump communicates problems through specific sensory signals. Grinding or whining noises during operation indicate blades struggling with waste or partial blockages restricting normal flow. While some operational noise is normal, elevated sounds combined with high amperage readings often signal discharge line obstructions requiring attention.
Foul odors near your pump system indicate worn seals allowing wastewater smells to escape or stagnant waste decomposing within the holding tank. Visible leaks around the pump or piping provide clear evidence of gasket failures, cracked components, or deteriorating connection points that need immediate attention to prevent environmental contamination.
Troubleshoot Alarm System Activation Issues
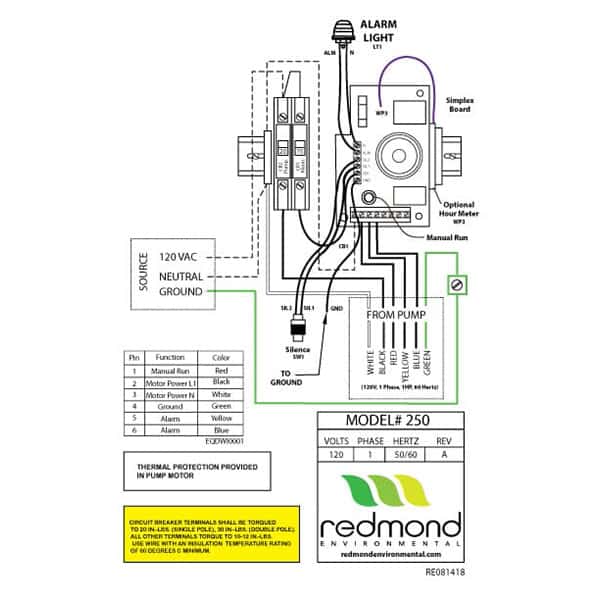
Modern grinder pump systems include alarm panels that alert you to developing problems before complete failure occurs. Understanding how to interpret these alerts enables faster resolution of underlying issues.
Fix Alarm Activation With No Pump Operation
When your alarm sounds but the pump fails to operate, begin by assessing voltage at the electrical quick disconnect. Compare measured voltage against nameplate specifications—many residential grinder pumps require 240 volts and cannot operate properly on 208-volt systems. Inadequate voltage prevents proper starting and running, causing alarm activation without pump operation.
Inspect the breather component for plugging or damage, as obstructed breathers prevent proper pressure equalization. Some systems use Gore-Tex breathers that require replacement rather than cleaning when clogged. Verify fluid levels match system requirements, as low levels may indicate alarm wiring problems rather than actual pump malfunction.
Resolve Frequent False Alarms
Frequent alarm activation without obvious problems suggests systemic issues requiring investigation. Evaluate whether your pump handles more wastewater than its designed capacity—perhaps from hot tub drainage, sump pump connections, or groundwater infiltration through compromised seals. These additional flows trigger alarms designed to detect abnormal operating conditions.
Inspect venting systems for partial obstructions, as even minor restrictions can cause false alarms. Check sensing lines for tightness and integrity by removing the pump and examining sensing bells for proper sealing. Test amperage to identify worn stators (typically showing low readings) or line obstructions (usually producing elevated readings).
Address Electrical Problems Causing Breaker Tripping
Electrical issues cause or contribute to many grinder pump failures. Systematic electrical troubleshooting identifies and resolves these problems efficiently before they lead to complete pump failure.
Stop Repeated Circuit Breaker Tripping
When your breaker trips repeatedly after pump operation, compare the pump’s nameplate amperage against the circuit breaker rating. Breakers sized too close to the pump’s running amperage may trip during startup surges, especially if a higher-capacity replacement unit was installed. Circuit wiring and breakers should be sized to at least twice the nameplate amperage rating.
Investigate short cycling patterns where the pump starts and stops frequently, as this stresses electrical components and causes breaker tripping. This pattern may result from an undersized holding tank, float switch problems, or actual high wastewater inflow. Check for mechanical binding within the pump—hair, debris, or damaged components can jam the grinding mechanism, forcing the motor to work against resistance and overload the circuit.
Verify Proper Electrical Connections
Inspect all wiring connections for looseness, corrosion, or damage, paying special attention to buried wiring that may suffer from ground movement, moisture intrusion, or age-related insulation failure. Assess control panel components including relays, sensors, and alarm circuits for water damage or component aging—wet controls require replacement rather than repair.
Confirm pump specifications match your electrical system requirements. Grinder pumps require dedicated breakers sized appropriately for their amperage needs. When breaker amperage approaches or falls below the pump’s requirements, the breaker may trip during startup attempts, requiring electrical system upgrades.
Eliminate Common Clogs and Blockages

Clogs represent the most frequent cause of grinder pump malfunction and require specific troubleshooting approaches to resolve without causing further damage.
Clear Float Switch Obstructions
The float switch controls pump activation based on wastewater level. Check if the float is covered in grease, debris, or solid waste preventing proper movement. When obstructed, the float may fail to trigger pumping or cause inappropriate activation. Gently clean the float mechanism without forcing movement to avoid damaging delicate components.
Never introduce inappropriate materials to your system—cooking oil and grease, cat litter, hygiene products, flushable wipes, paper towels, large food scraps, or non-biodegradable items create substantial blockages. These materials accumulate within pipes and the holding tank, restricting flow and overworking the pump motor.
Remove Clots and Silt Buildup
Unlike traditional clogs from large debris, clots consist of smaller particles and silt building up along interior walls of the pump and pipes. This accumulated material catches passing waste, gradually restricting system capacity. Clots develop silently, with homeowners often only noticing when the pump begins running more frequently or producing unusual noises.
When clots form, the pump works harder and longer to process normal wastewater volumes, accelerating wear on internal components. Professional pumping and cleaning are typically required to remove established clots that persist after basic troubleshooting attempts.
Prevent Future Grinder Pump Failures

Proactive maintenance extends your grinder pump’s lifespan and prevents expensive emergency repairs. Implement these specific measures to protect your investment before problems develop.
Follow Critical Maintenance Practices
Monitor pump runtime—average household wastewater generation of 250 gallons daily should result in less than 15 minutes of pump operation per day. Significantly elevated running times indicate developing problems requiring attention. Inspect the control panel regularly for alerts or malfunction indicators that provide early warning of issues.
Install proper drainage depth below the frost line to prevent freezing problems in colder climates. Ensure your electrical system is sized appropriately with circuit breakers rated at least twice the pump’s nameplate amperage. Install a check valve in the discharge line to prevent backflow into the pump after each cycle.
Schedule Professional Inspections
Annual or bi-annual professional servicing catches wear before it leads to complete pump failure. Professionals perform thorough cleaning, component inspection, and efficiency testing beyond typical homeowner capabilities. When pumps exhibit signs of severe damage—including burning smells or evidence of overheating—immediate professional assessment is necessary.
Residential grinder pumps typically last around 8 years with proper maintenance. Pumps failing well before this timeframe warrant professional investigation to identify root causes preventing recurrence. Complex electrical problems, buried wiring faults, or severe clogs require licensed technicians rather than DIY troubleshooting attempts.
By following these specific troubleshooting steps and prevention strategies, you can address minor grinder pump issues before they escalate into expensive emergencies. Regular maintenance, proper use habits, and prompt attention to warning signs keep your waste management system running reliably for years to come—protecting your home from the health hazards and property damage caused by sewage backups.





