Air grinder repair requires specialized knowledge to maintain safe operation of these high-speed pneumatic tools. When your air grinder stops delivering the consistent power needed for metalworking, automotive repair, or fabrication tasks, understanding proper repair protocols becomes critical. Many technicians face common issues like sudden power loss, unusual vibrations, or air leaks that compromise performance and safety. This guide outlines essential considerations for air grinder maintenance while directing you to legitimate repair resources that keep you and your equipment safe.
Why Proper Air Grinder Repair Matters
Improperly repaired air grinders create significant safety hazards in workshops and industrial settings. These tools operate at speeds exceeding 20,000 RPM, generating tremendous centrifugal force that can cause catastrophic failure if internal components aren’t correctly maintained. A single compromised bearing or worn vane can lead to wheel detachment—a potentially fatal situation. Professional repair preserves the tool’s engineered safety features while maintaining warranty coverage that DIY fixes often void. Understanding when to seek professional service versus performing basic maintenance could prevent serious injury while extending your tool’s service life.
Critical Safety Precautions Before Any Repair Attempt
Disconnect Power Source Properly
Always disconnect the air supply hose and bleed residual pressure before beginning any repair work. Simply turning off the compressor isn’t sufficient—trapped air in the tool’s internal chambers can cause unexpected activation during disassembly. Verify complete pressure release by briefly squeezing the trigger after disconnecting. Working on pressurized pneumatic tools risks sudden, uncontrolled rotation that can cause severe hand injuries from moving parts.
Essential Personal Protective Equipment
Wear safety glasses with side shields, cut-resistant gloves, and hearing protection even during repair work. Small metal components under spring tension can become projectile hazards when released during disassembly. The confined spaces inside air grinders often contain sharp edges from worn components that can easily cut unprotected hands. Maintain a clean, well-lit workspace with magnetic trays to organize small parts and prevent loss.
Common Air Grinder Problems You Can Diagnose
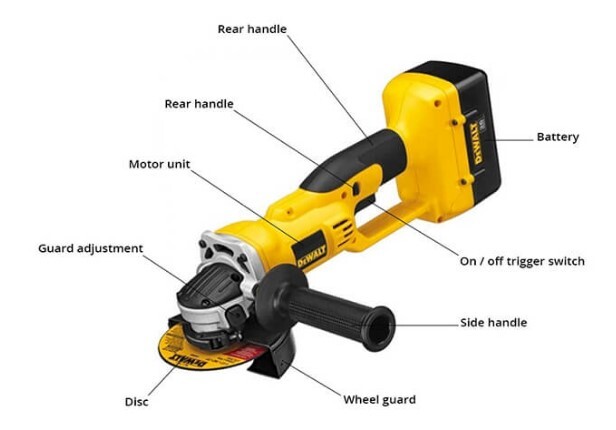

Power Loss and Speed Reduction
When your air grinder struggles to maintain speed under load, examine these potential causes before disassembly. Restricted airflow from kinked hoses or clogged filters often mimics internal problems. Verify your compressor delivers sufficient CFM at the required PSI for your specific grinder model—most require 90 PSI minimum with 4-6 CFM capacity. Check for air leaks at hose connections using soapy water solution before assuming internal component failure.
Unusual Noise and Vibration Patterns
Distinctive sounds indicate specific problems in pneumatic grinders. A high-pitched whine typically signals bearing failure, while rhythmic knocking often points to damaged vanes or rotor imbalance. Excessive vibration during operation frequently results from worn spindle bearings or misaligned internal components. Document the specific sound characteristics and when they occur (during startup, under load, etc.) to help professionals diagnose issues accurately.
When to Seek Professional Repair Services
Complex Internal Component Failures
Motor assembly repairs involving rotors, vanes, and cylinders require precision measurement tools and manufacturer specifications that most technicians lack. These components operate with tight tolerances measured in thousandths of an inch—improper clearance measurements lead to premature failure. Professional repair centers maintain calibrated gauges and access to OEM parts that ensure proper fit and function. Attempting these repairs without proper tools often causes more damage than the original problem.
Warranty Coverage Considerations
Most major air grinder manufacturers void warranties when unauthorized repairs occur. Even simple bearing replacements require specific installation tools to avoid housing damage. Before disassembling a relatively new tool, check warranty terms and locate authorized service centers. The cost of professional repair often proves less expensive than replacing a tool damaged by improper DIY repair attempts.
Essential Maintenance You Can Perform Safely

Air Filter and Inlet Screen Cleaning
Monthly maintenance prevents 80% of common air grinder problems. Remove the air inlet filter housing (typically a hex nut at the air hose connection point) and clean the brass screen inside using carburetor cleaner and a soft brush. Allow complete drying before reassembly—moisture in the air system accelerates internal corrosion. Replace foam inlet filters according to manufacturer schedules, usually every 50-100 operating hours in dusty environments.
Proper Lubrication Procedures
Add 4-5 drops of pneumatic tool oil into the air inlet before each use—a critical step many technicians overlook. Operate the tool briefly to distribute oil through the system before connecting grinding attachments. Never use standard motor oil, as it gumms up internal components. For extended storage, add extra oil and cycle the tool to coat internal surfaces. Over-lubrication causes excessive exhaust smoke and attracts debris, while under-lubrication accelerates vane and cylinder wear.
Finding Legitimate Repair Resources
Manufacturer Service Manuals
Reputable air grinder manufacturers provide detailed service manuals for professional repair centers. Contact customer support with your tool’s model and serial number to request technical documentation. Brands like Ingersoll Rand, DeWalt, and Chicago Pneumatic maintain extensive service networks with properly trained technicians. These manuals contain critical torque specifications, exploded diagrams, and special tool requirements that ensure proper repair.
Authorized Service Center Locator
Use manufacturer websites to find certified repair facilities near you—most provide online locators by ZIP code. Authorized centers maintain original equipment manufacturer parts inventories and receive regular technical updates about model-specific issues. They often offer loaner tools during repair periods for professional users who depend on these tools daily. Verify technician certifications before entrusting valuable equipment to any repair service.
Preventing Future Air Grinder Failures
Air Quality Management System
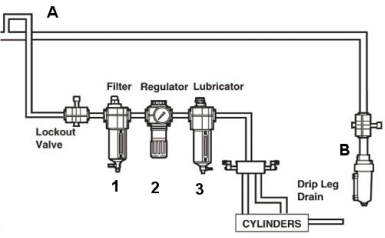
Install a dedicated air preparation system at your workstation featuring a filter-regulator-lubricator (FRL) unit sized for your tool’s CFM requirements. This three-stage system removes moisture, regulates pressure, and injects precise lubrication amounts into the air stream. Moisture causes internal rust that damages precision components, while inconsistent pressure leads to erratic performance. Proper air preparation extends tool life by 300% according to industry studies.
Proper Storage and Handling Protocols
Store air grinders with protective caps on the spindle and air inlet to prevent debris entry. Hang tools vertically rather than laying them flat to maintain internal component alignment. Before storage, operate the tool briefly to expel moisture and apply protective oil coating. Transport grinders in padded cases rather than tossing them in toolboxes where impacts can misalign sensitive internal components.
Final Note: While basic maintenance keeps air grinders operating efficiently, complex repairs require manufacturer specifications and specialized tools. The high rotational speeds and precision engineering of pneumatic grinders demand proper repair procedures that prioritize safety above all else. Consult your tool’s manufacturer for legitimate service resources rather than risking injury with improvised repair methods. Regular preventative maintenance following manufacturer guidelines provides the best return on your pneumatic tool investment while ensuring safe workshop operation.





